# COMP 2540 - Midterm
# Algorithm Analysis
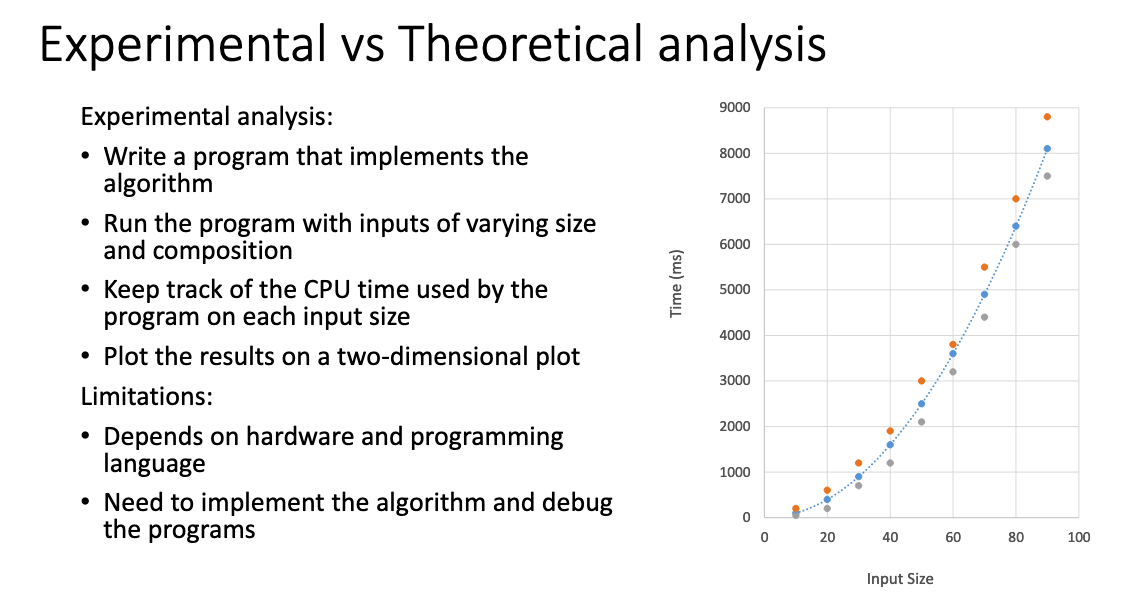
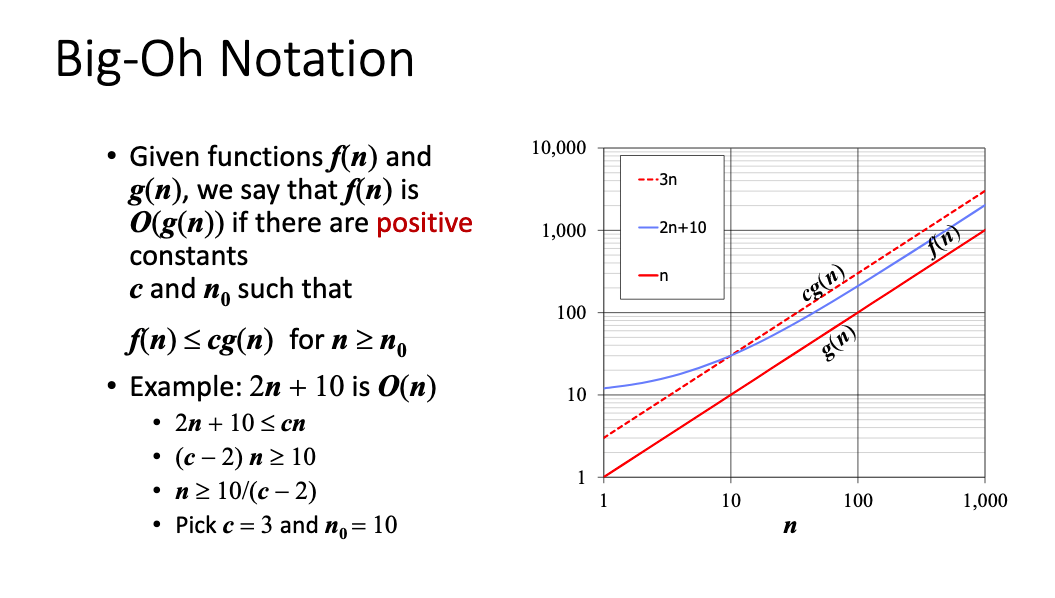
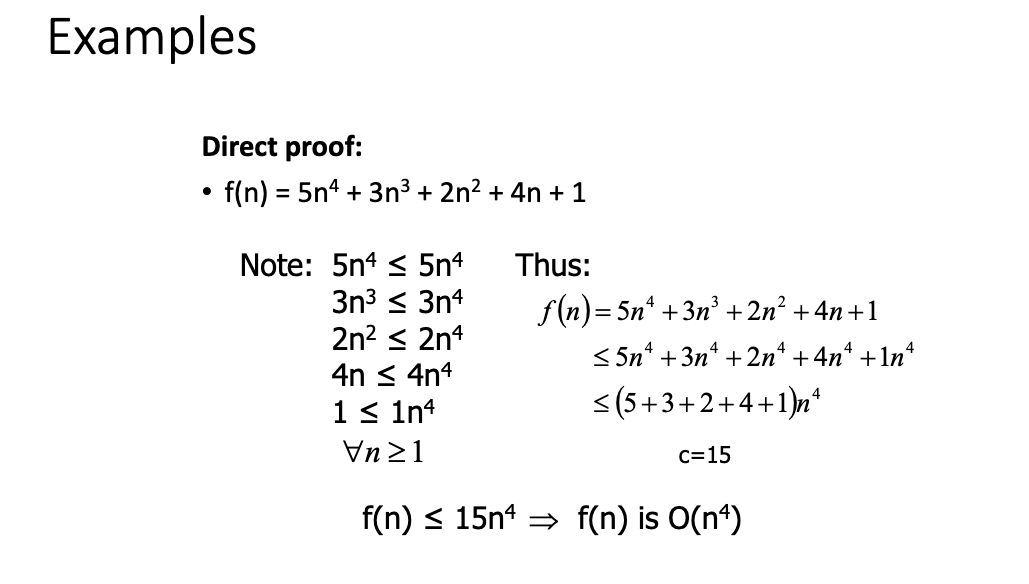
- An algorithmis a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem in a finite amount of time.

- Performance of an algorithm is measured in terms of the input size
- The running time of an algorithm typically grows with the input size.
- Average case time is often difficult to determine.
- We focus mostly on the worst-case running time.

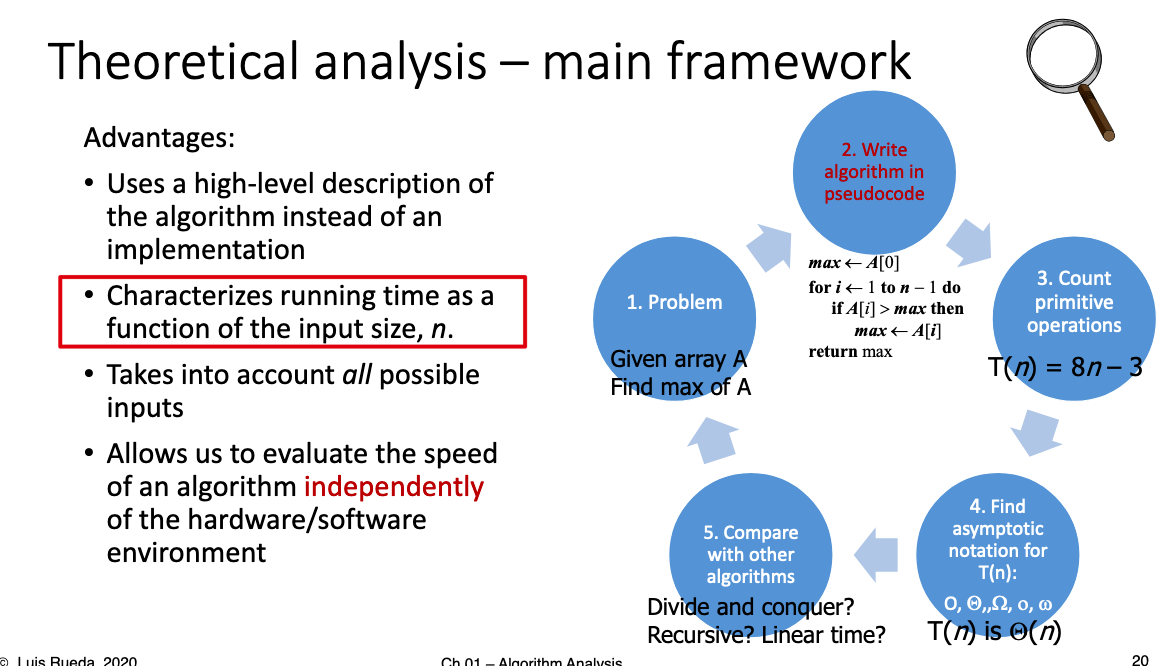
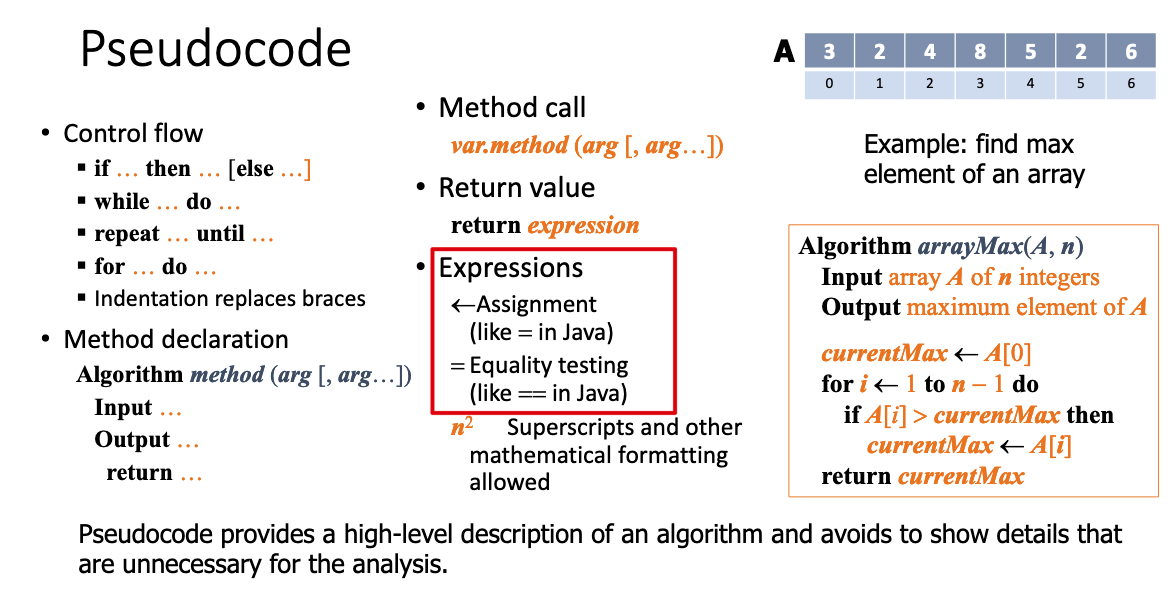
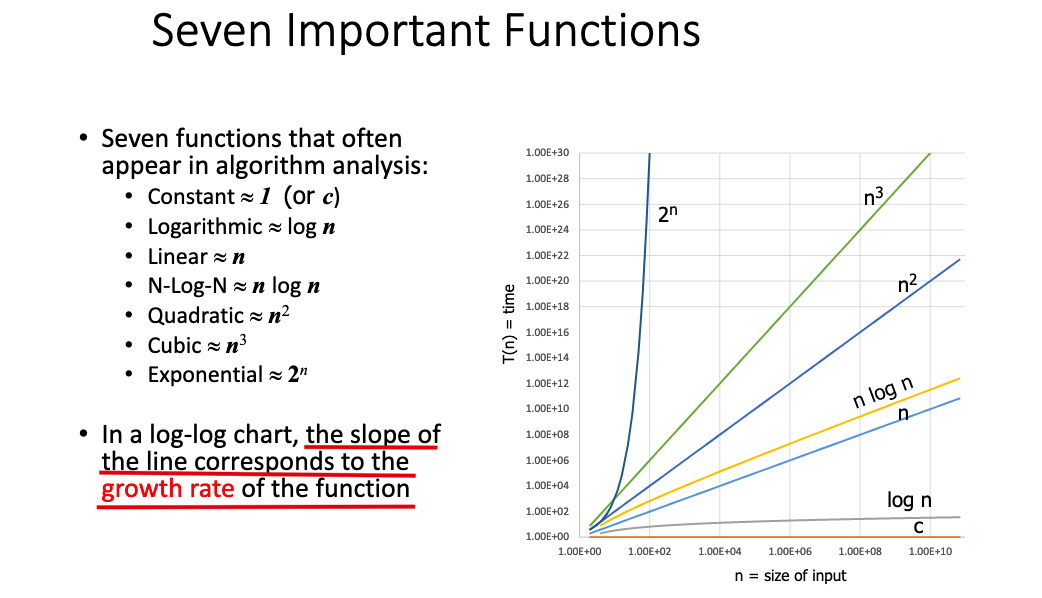
- The growth rate is not affected by:
- constant factors
- lower-order terms
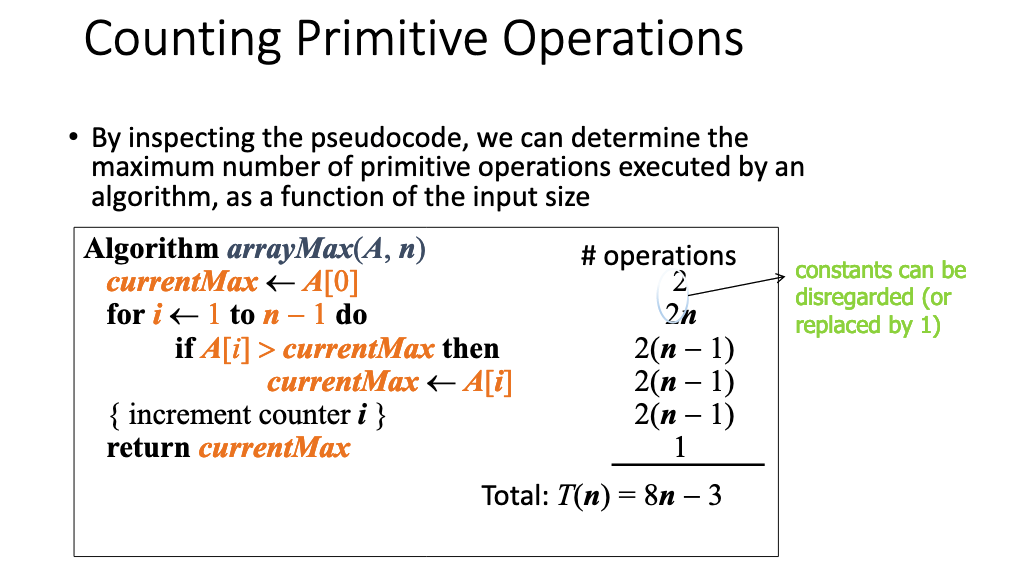




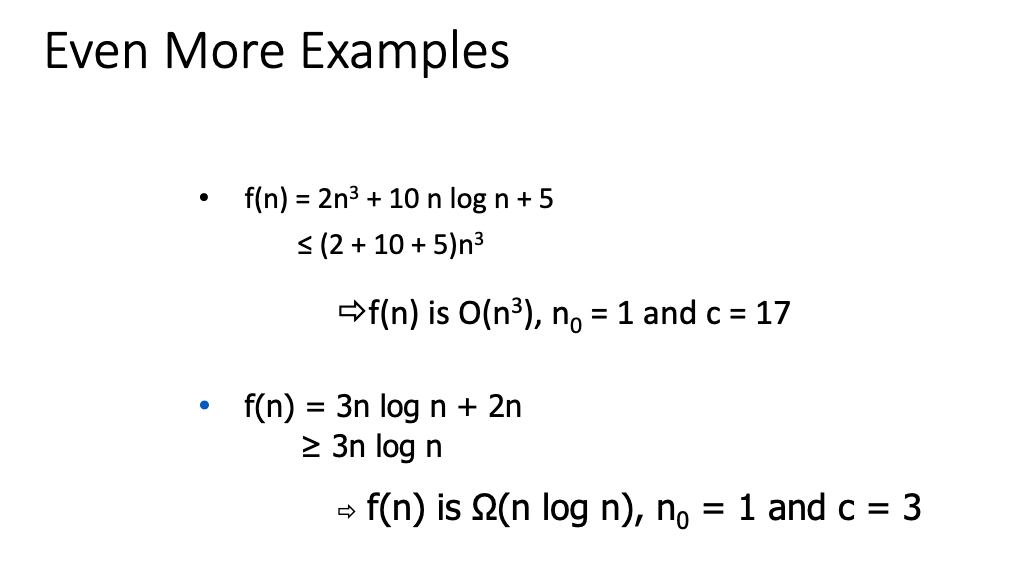
# Stacks Queues
# 1.What is an ADT? Give examples.
- Def.:An abstract data type (ADT) is a set of objects with a set of operations.
- 它指定了一组数据值的集合及可作用在这些数据值上的一组操作;
- Examples of ADTs:
- Lists, stacks, queues
- Sets
- Trees, Graphs
- Operations:
- Add, insert, push, enqueuer, remove, delete, dequeue, pop, contains, union, find, etc
# 2.What are the main advantages and disadvantages of the array-based stack? Likewise for the linked-list-based stack.

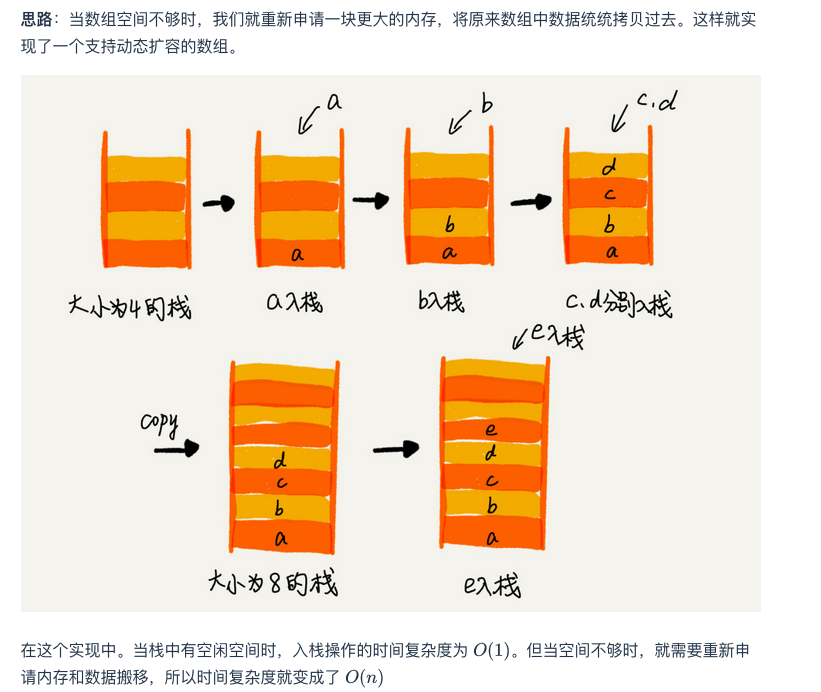
# 3.Discuss a solution for the case in which the array-based stack becomes full.
# 4.Give an example of (each) correct and incorrect bracket matching.


# 5.Give examples of other HTML tags that can be matched using the HTML Tag Matching Algorithm.

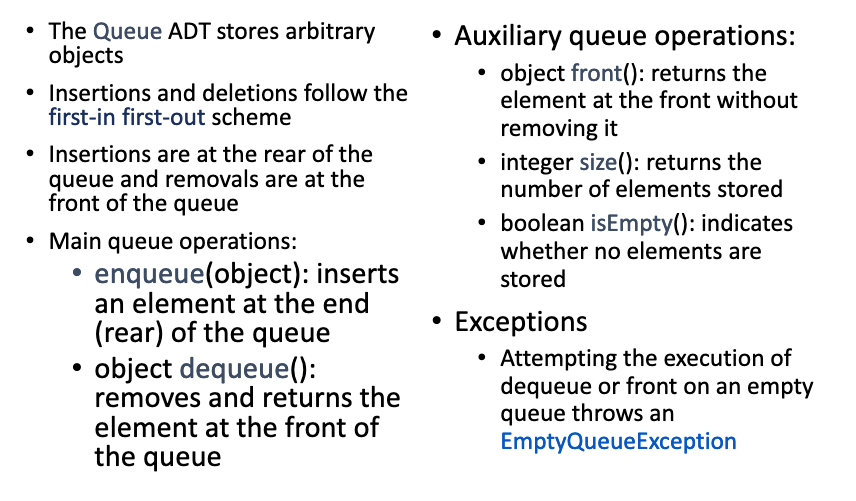
# 7.What is the queue ADT? Give examples.
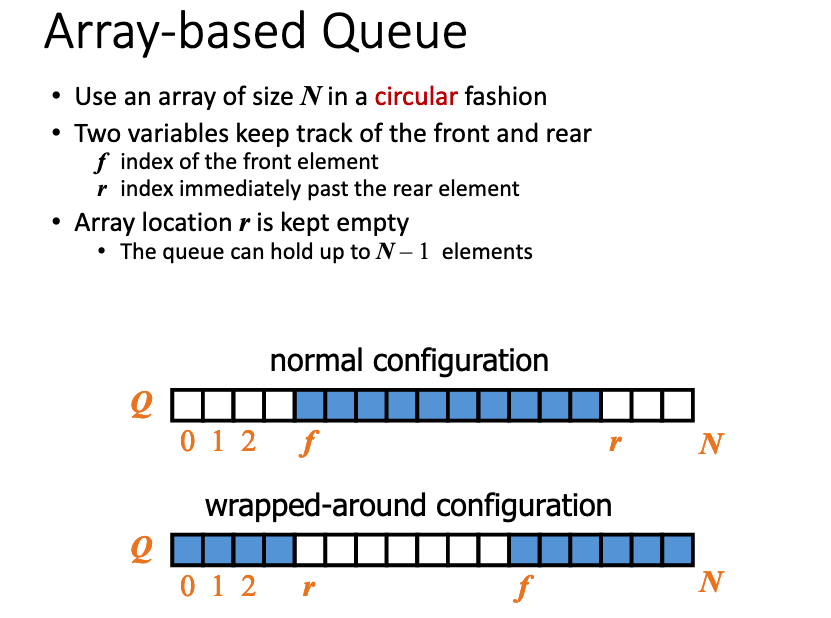
# 8.What are the main advantages and disadvantages of the array-based queue? Like wise for the linked-list-based queue.

# Linked List
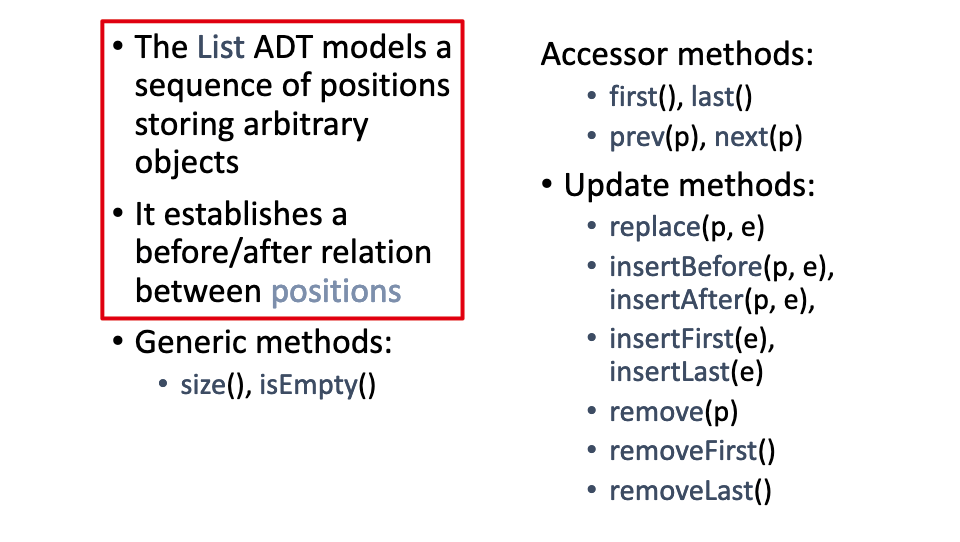
# 1.Give the main features of the List ADT.
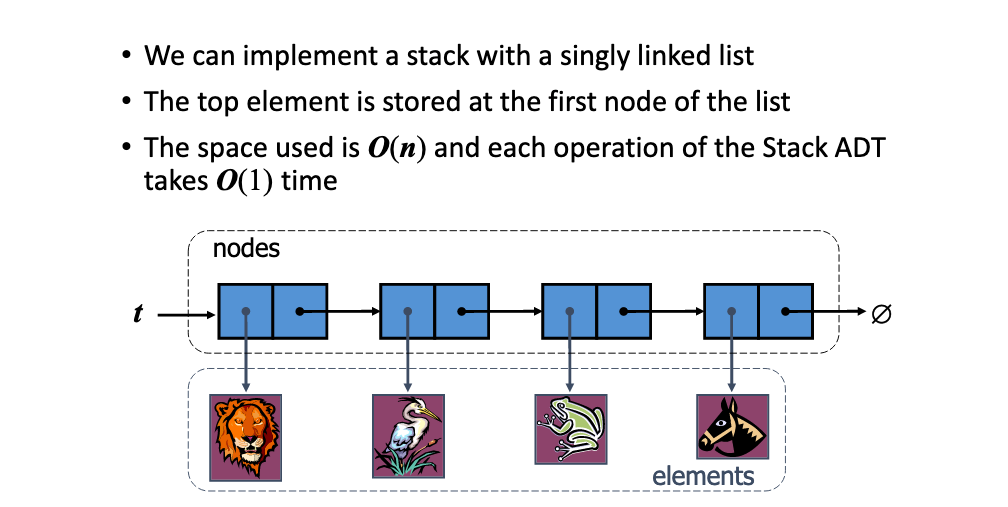
# 4. Describe the implementation of a stack in a singly-linked list. What about a queue.

// LinkedList
package Assignment2;
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
private int count;
// constructor
public LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.count = 0;
}
// addFirst
public void addFirst(Object data) {
Node n = new Node(data);
// if Head and Tail point to null
// Both head and tail point to the new node
// and the new node points to null
if (tail == null && head == null) {
head = n;
tail = n;
} else {
// link the new node to its successor
// link head to the new node
n.setNext(head);
head = n;
}
count++;
}
// removeFirst
public Node removeFirst() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("Error: the list is empty!");
return null;
}
Node n = head;
// head points to next node
head = n.getNext();
// Allow garbage collector to reclaim the former first node
n.setNext(null);
count--;
return n;
}
// addLast
public void addLast(Object data) {
Node n = new Node(data);
// if Head and Tail point to null
// Both head and tail point to the new node
// and the new node points to null
if (tail == null && head == null) {
head = n;
tail = n;
} else {
// the old last node point to new node
tail.setNext(n);
// update tail to point to the new node
tail = n;
}
count++;
}
// removeLast
public Node removeLast() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("Error: the list is empty!");
return null;
}
Node current = head;
Node previous = null;
// find the last node, and the node before it;
while (current.getNext() != null) {
previous = current;
current = current.getNext();
}
// set the previous node to point to null
previous.setNext(null);
count--;
return current;
}
// getFirst
public Node getFirst() {
return head;
}
// getLast
public Node getLast() {
return tail;
}
// size
public int size() {
return count;
}
}
// LinkedStack
package Assignment2;
public class LinkedStack {
private LinkedList list = null;
public LinkedStack() {
this.list = new LinkedList();
}
public void push(Object data) {
list.addFirst(data);
}
public Node pop() {
return list.removeFirst();
}
public Node top() {
return list.getFirst();
}
public int size() {
return list.size();
}
public Boolean isEmpty() {
if (list.size() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
// LinkedQueue
package Assignment2;
public class LinkedQueue {
private LinkedList list = null;
public LinkedQueue() {
this.list = new LinkedList();
}
public void enqueue(Object data) {
list.addLast(data);
}
public Node dequeue() {
return list.removeFirst();
}
public Node front() {
return list.getFirst();
}
public int size() {
return list.size();
}
public Boolean isEmpty() {
if (list.size() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
# Array Lists
# 1.Give the main features of the Array List ADT.
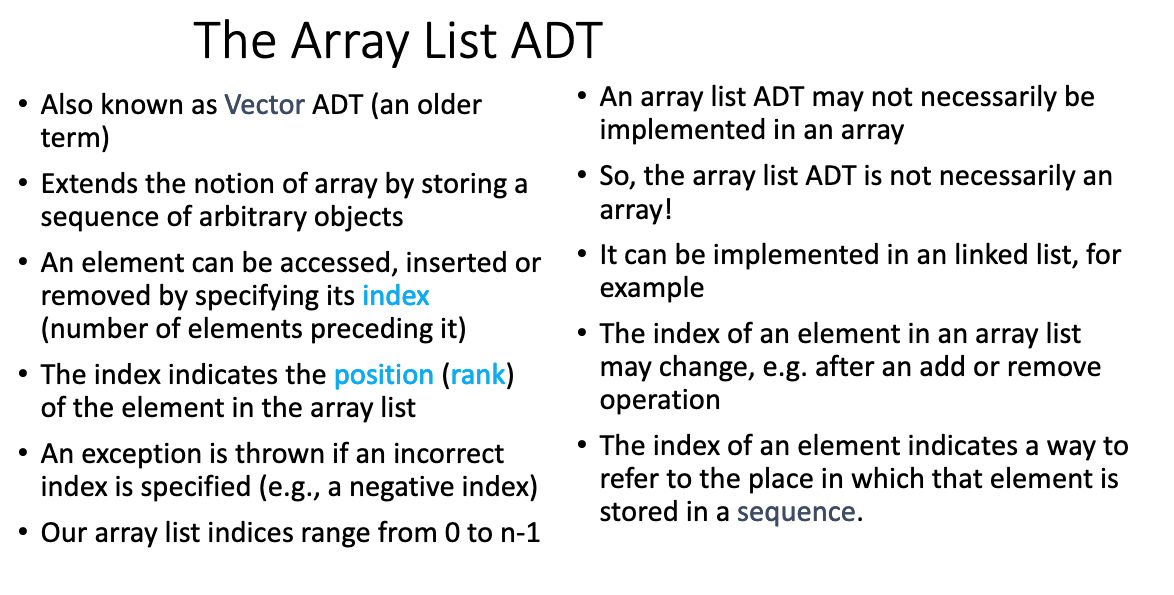

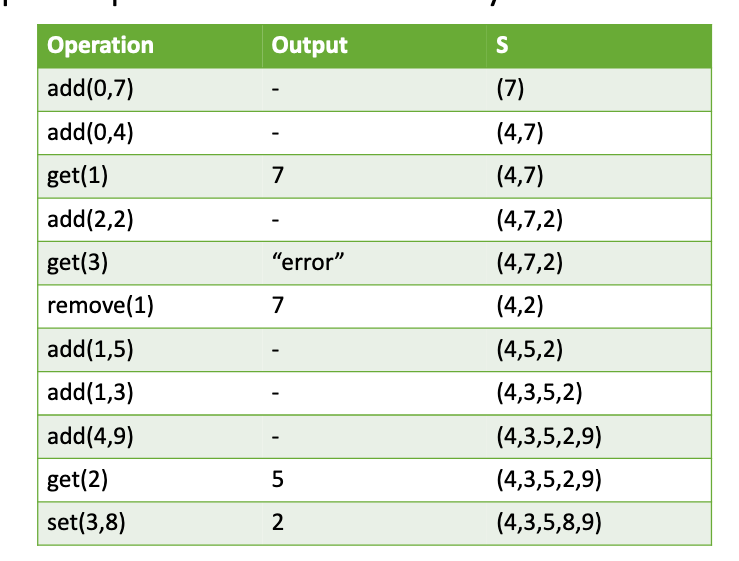
# 2.Discuss the main differences between the array and the linked list implementations of an ArrayList

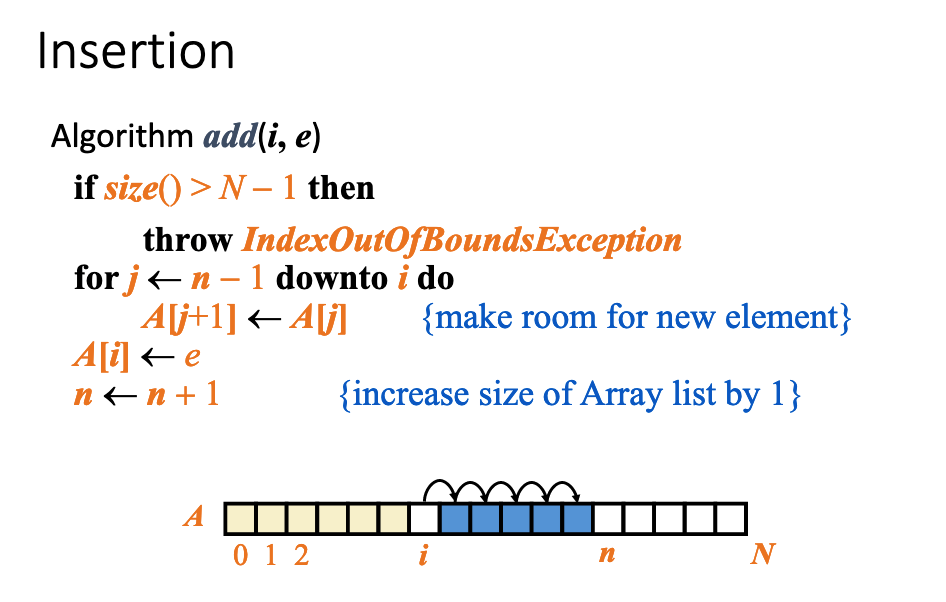
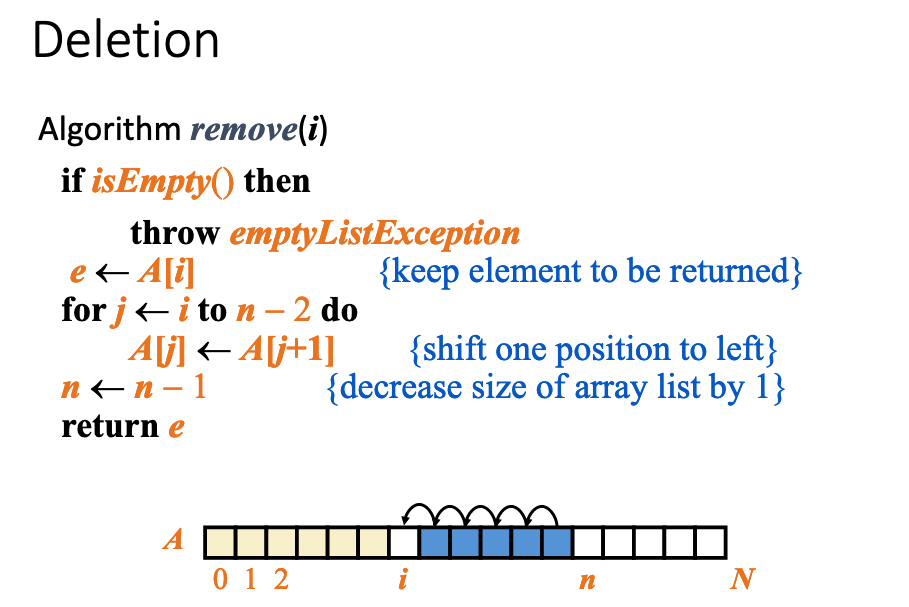

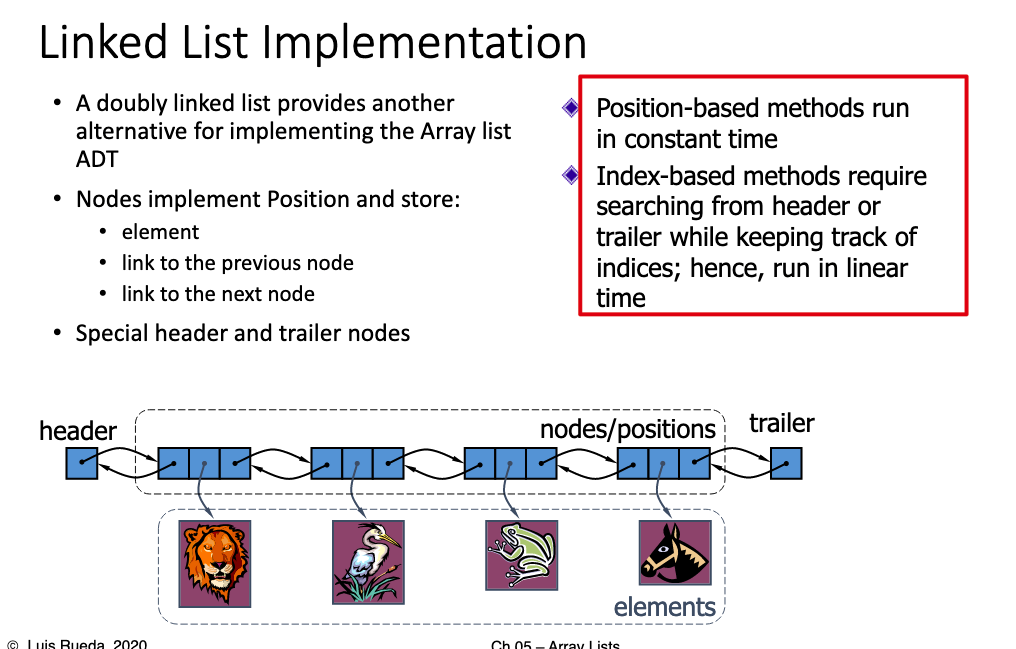
# 3.Consider the table of slide 19. Give explicit reasons (justifications) of why some operations have different running times for the array vs linked list implementations.
# 4.Why would you use a circular array for an Array List? Will the running times of the main operations change?
# 5.Give an example in which you have to use the linked list implementation of the Array List. Discuss the solution
# Recursion
# 1.Explain how a generic recursive algorithm works, and why the base case(s) is/are needed.
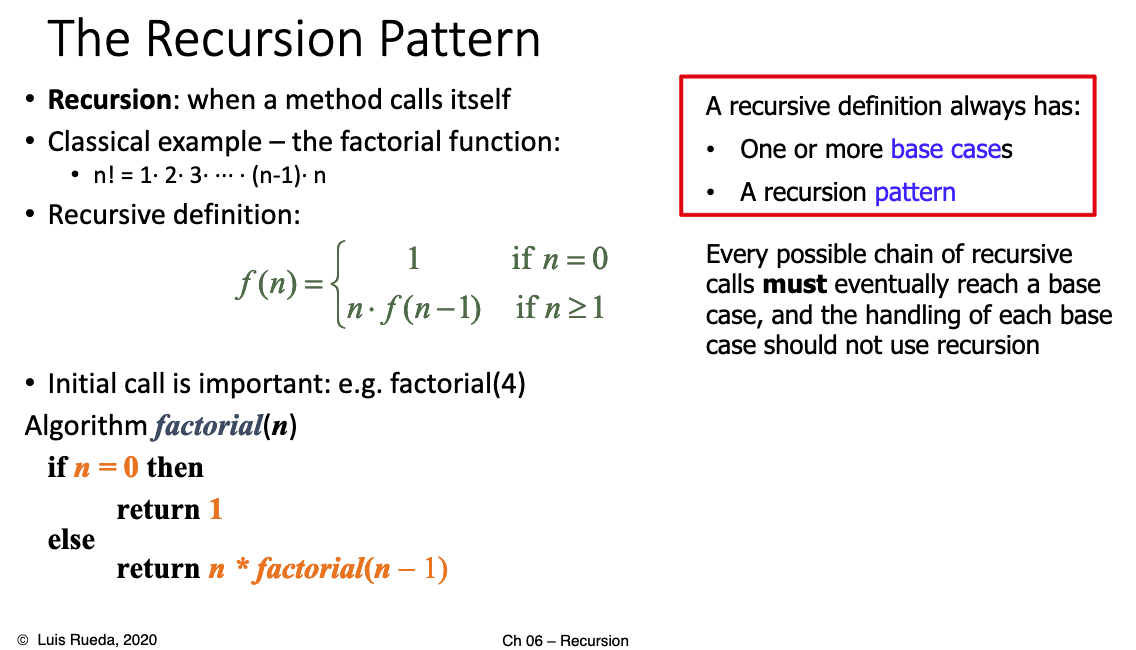
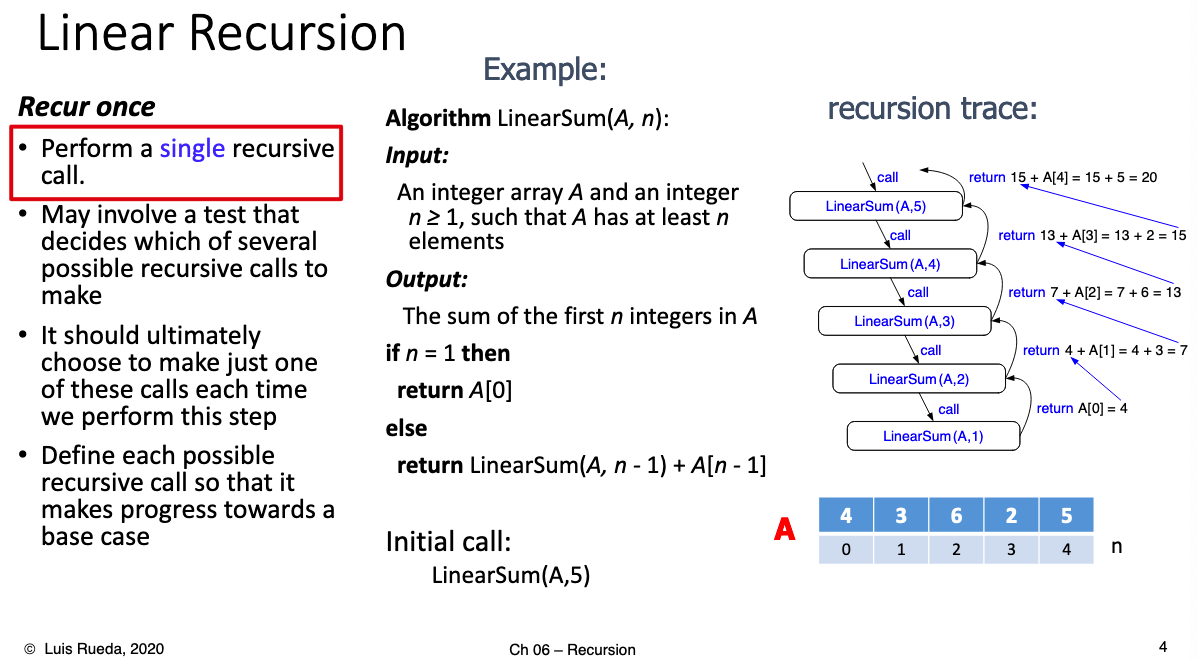
# 2.What are the types of recursion studied in this chapter? What is linear recursion? binary?

# 3.Trace factorial(10). Show all steps.

# 5.Explain why computing powers run in O(log n), in the worst case.

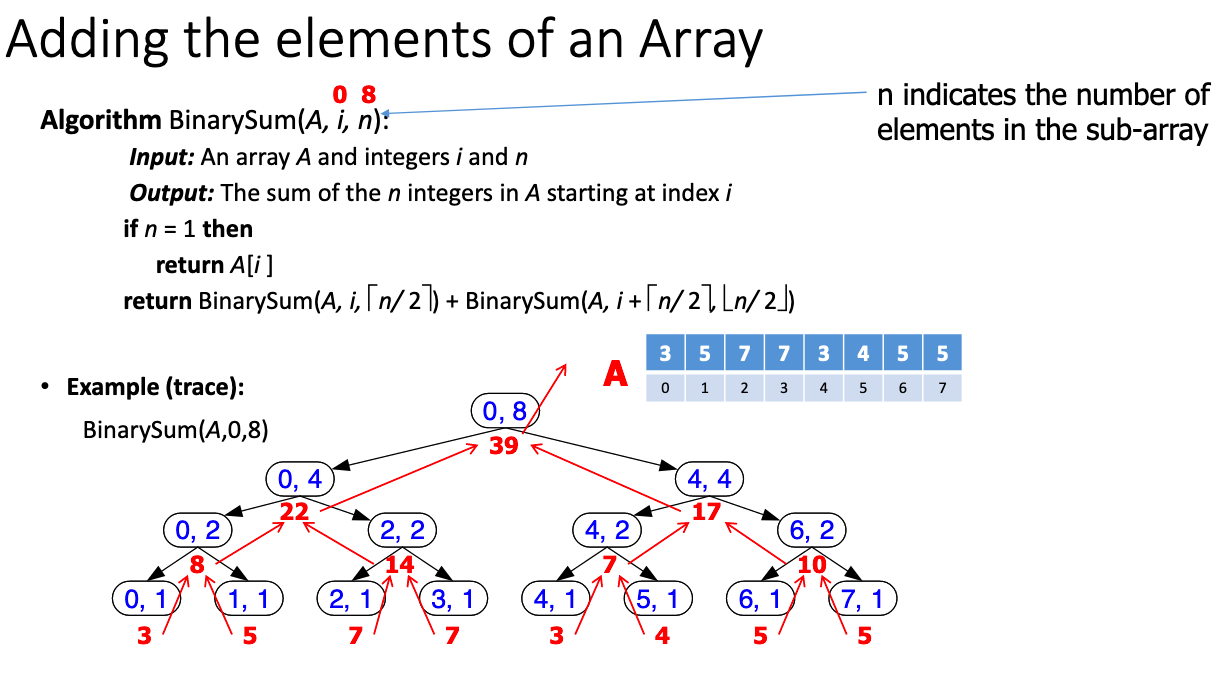
# 6.What is the worst case running time of binary sum? Why isn’t it O(log n)?
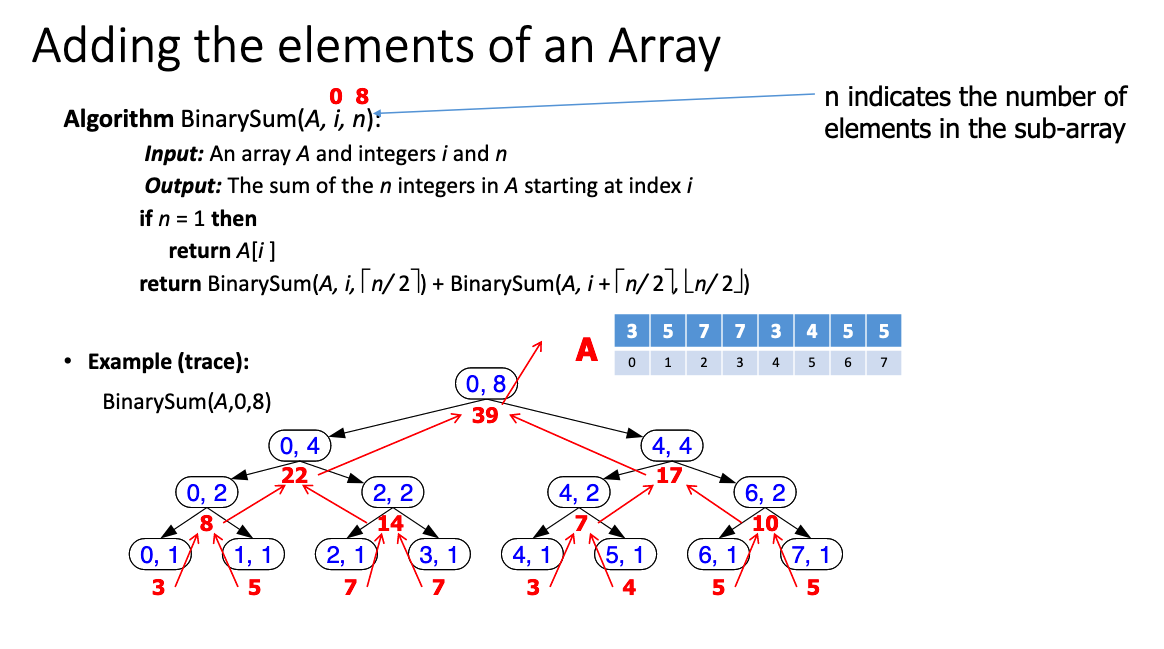
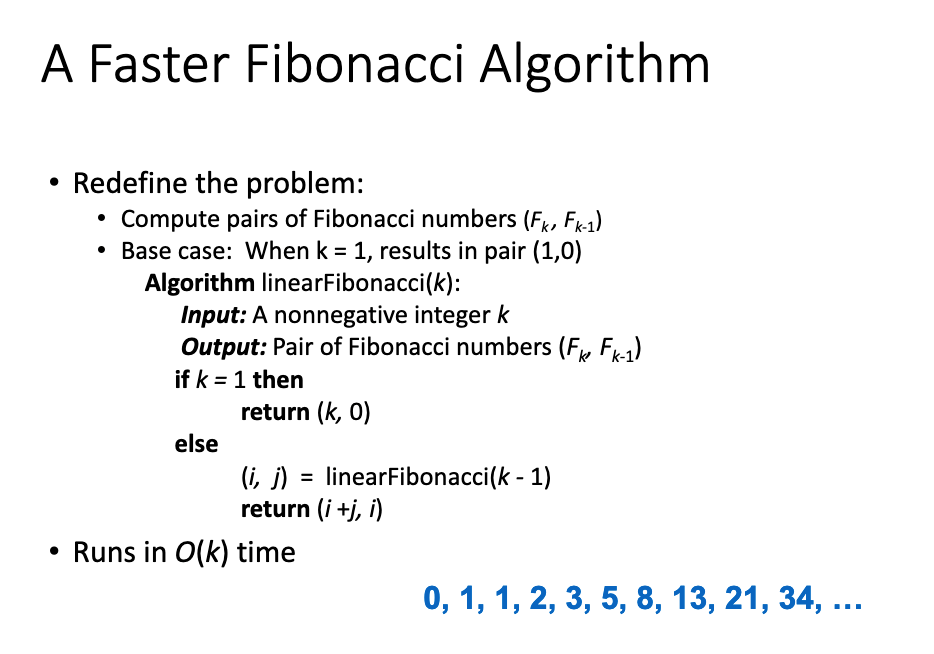
# 7.Explain why linearFibonacciruns in linear time, i.e., O(k).
# Priority Queues
# 1.What are the main differences between a queue and a priority queue?
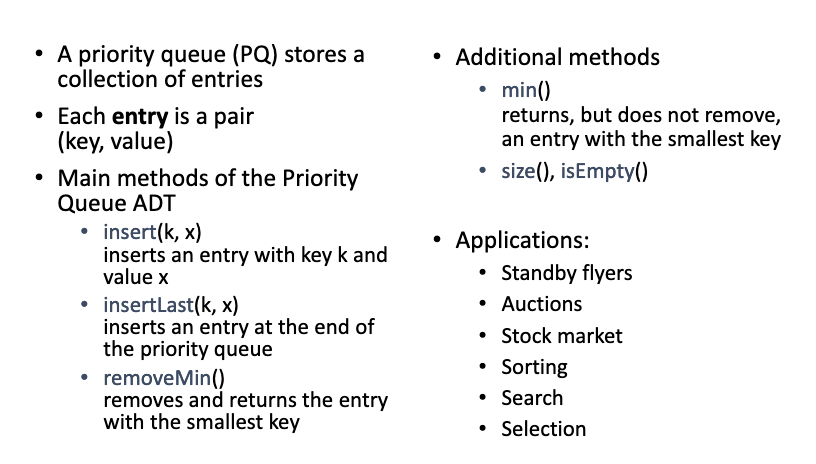
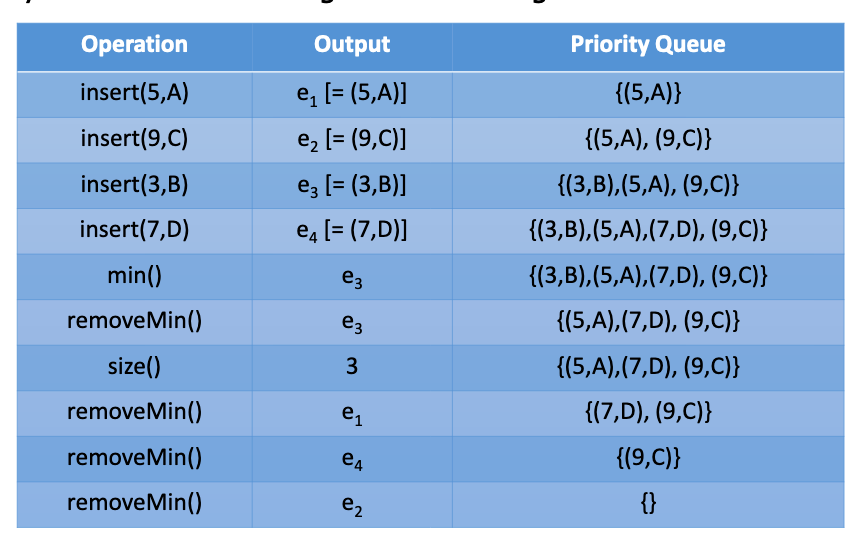
- 普通的队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,元素在队列尾追加,而从队列头删除。在优先队列中,元素被赋予优先级。当访问元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除。
- a priority queue is an abstract data type which is like a regular queue or stack data structure, but where additionally each element has a "priority" associated with it. In a priority queue, an element with high priority is served before an element with low priority.
# 2.What are the main properties of a total order relation?
- 全序关系是指给定集合上所有元素间都具有"序"关系


# 3.Give examples of two keys for which the result of the comparison is different depending on the data type

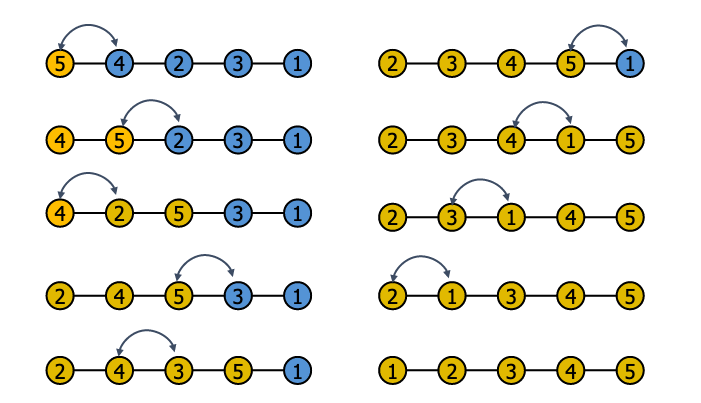
# 4.Sort [e, r, f, t, a, m, c] in increasing order by following insertion sort and selection sort. Show all the required steps. Do the same for the corresponding in-place versions of the algorithms.
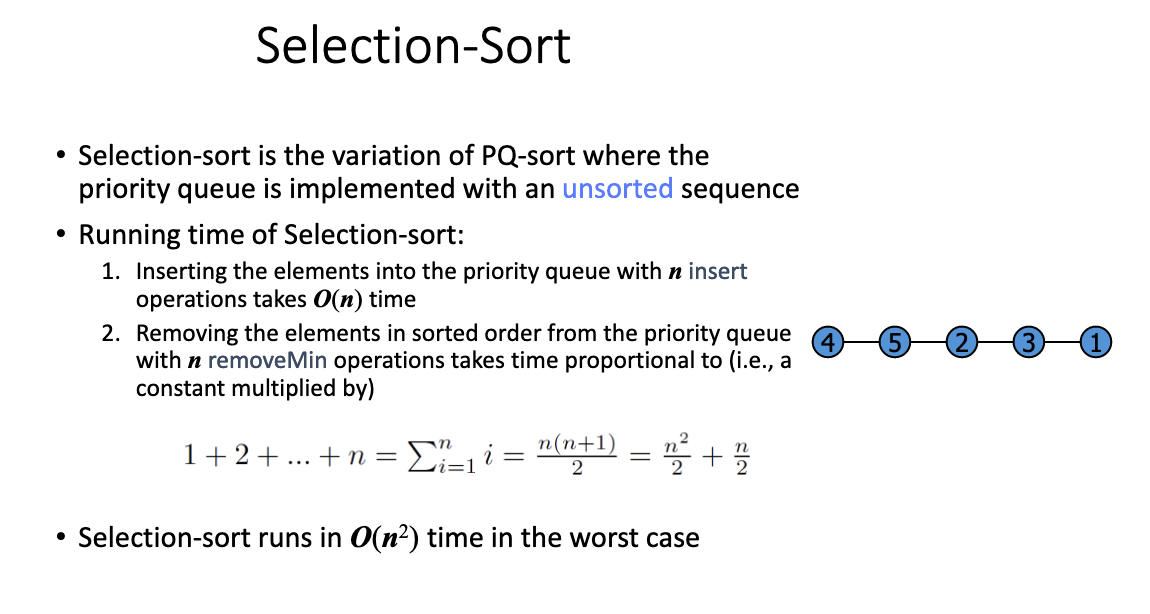
- 将数组中的数据分为两个区间,“已排序区间” 和 “未排序区间”;
- 从 “未排序区间” 中找到最小值并将其放置在 “已排序区间” 的末尾;
- 循环这个步骤,直至未排序区间为空;
void select_sort(int[] a, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
// 找到最小元素
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if(a[j] < a[minIndex]) minIndex = j;
}
// 交换最小元素与第一个未排序元素
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[minIndex];
a[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
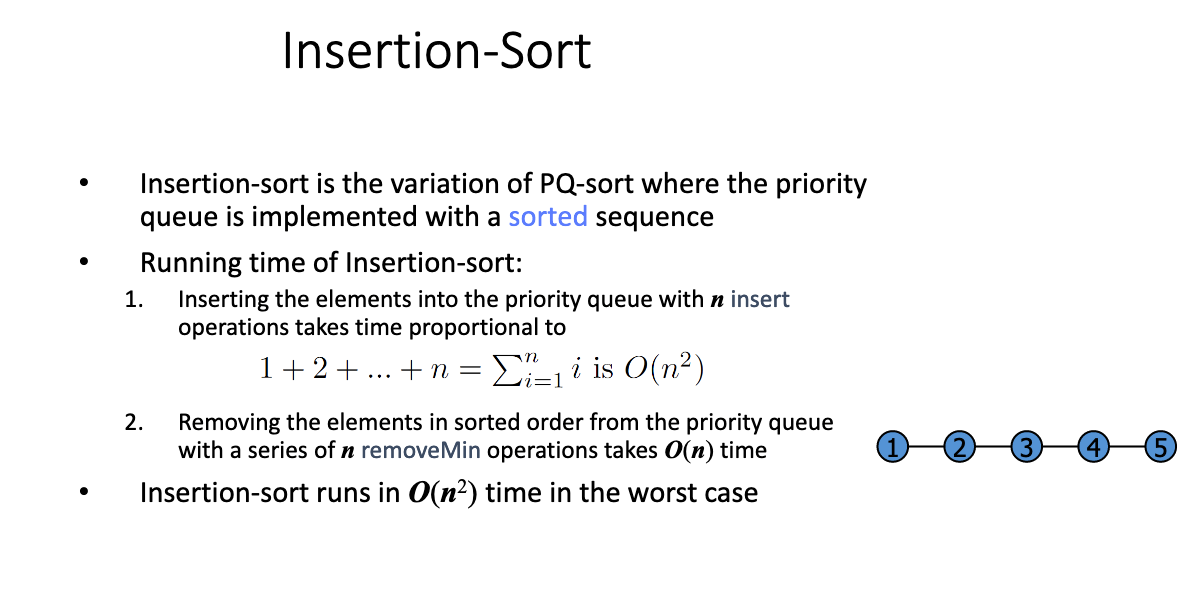
- 将数组中的数据分为两个区间,“已排序区间” 和 “未排序区间”;
- 初始已排序区间只有第一个元素;
- 依次将未排序区间中的元素,在已排序区间中找到合适的插入位置将其插入;
- 直至未排序区间为空;
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int n) {
int i, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int value = arr[i];
// find the position to insert item
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (value < arr[j])
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
else
break;
}
arr[j + 1] = value; // insert item
}
}
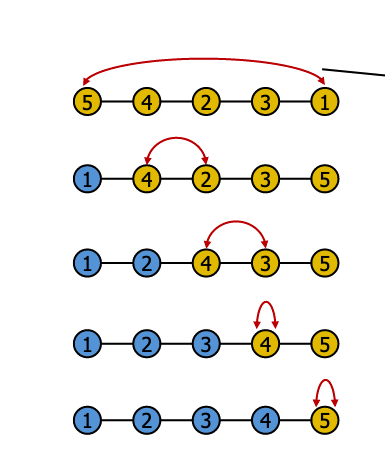
# Quick Sort

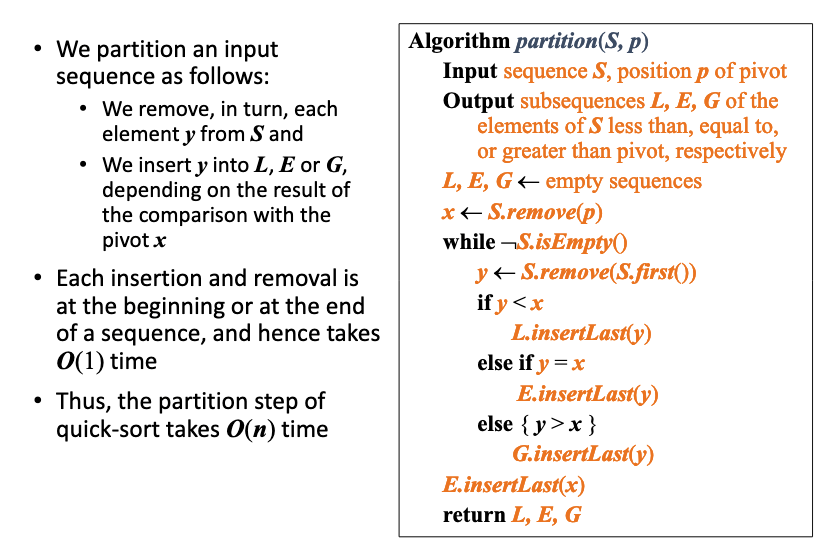
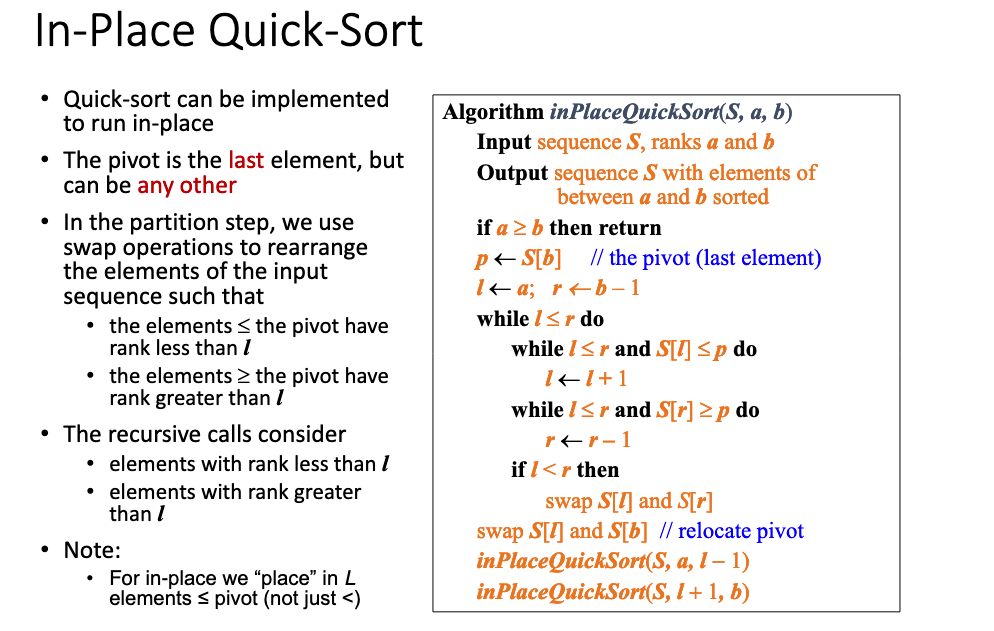



// quick sort
public static void quickSort(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right)
return;
// The Pivot is the last element
int pivot = a[right];
int i = left;
int j = right - 1;
while (i <= j) {
// Find an element that is greater then Pivot (from left to right)
while (i <= j && a[i] <= pivot) {
i++;
}
// Find an element that is less then Pivot (from right to left)
while (i <= j && a[j] >= pivot) {
j--;
}
// if left index is less than right index
// then, swap elements at indices left and right;
if (i < j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
// relocate pivot
// swap element at index i with the previous pivot
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[right];
a[right] = temp;
// use recursion to seperate the array to two part
// the first is the array that is less than pivot
// the second is the array that is greater than pivot
quickSort(a, left, i - 1);
quickSort(a, i + 1, right);
}
# Merge Sort

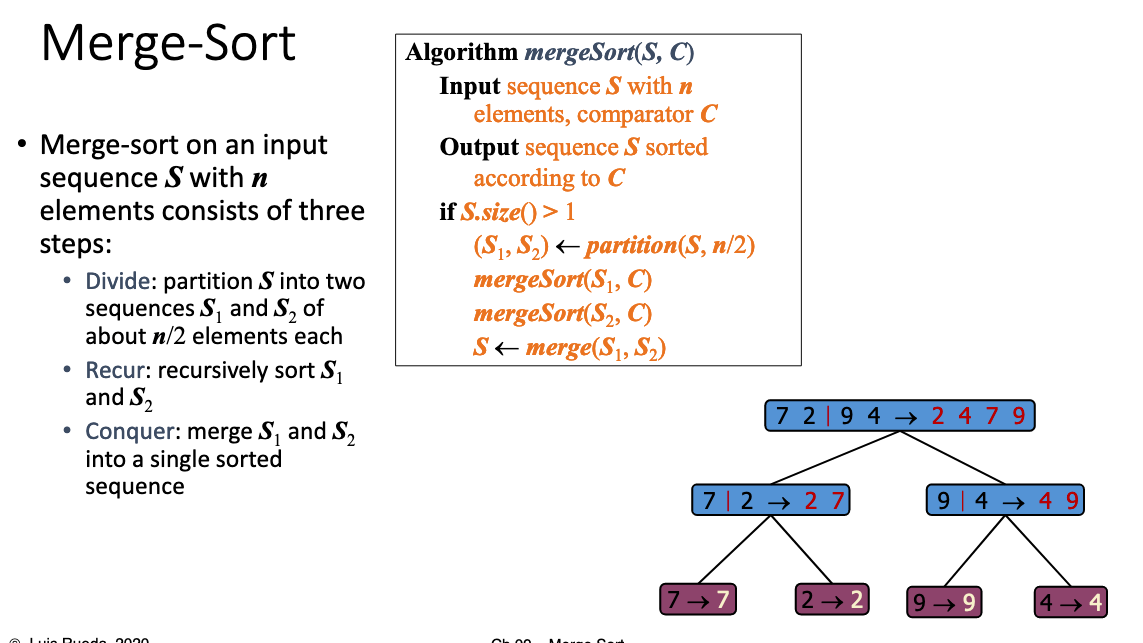
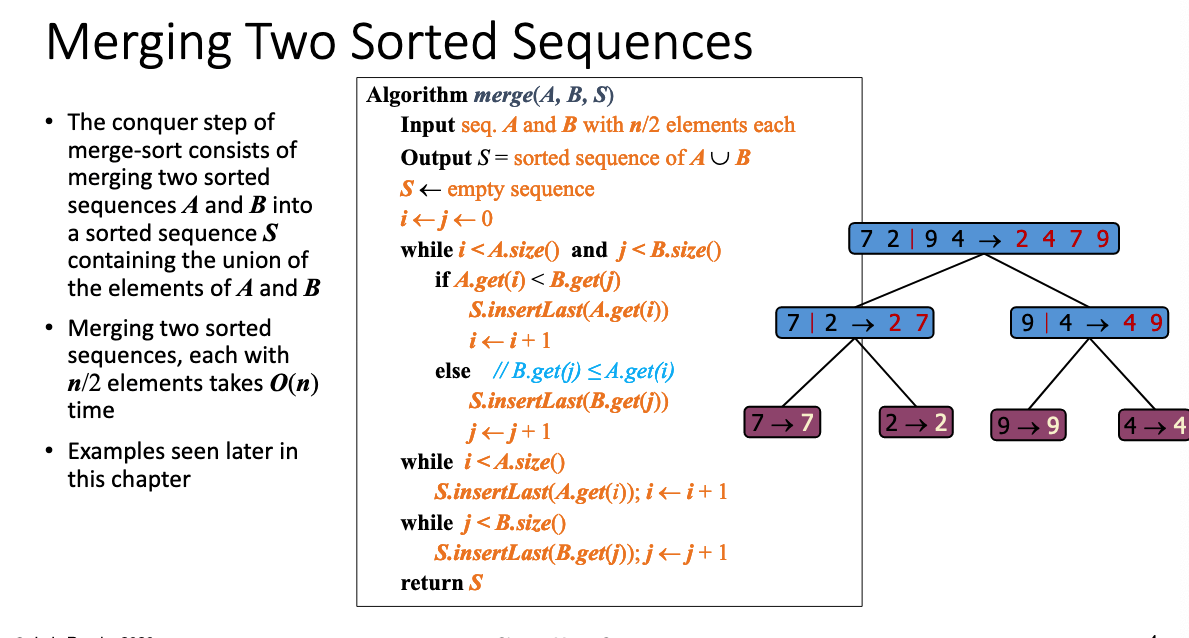
public static void merge_sort(int[] a, int n) {
divide(a, 0, n - 1);
}
// 切分
public static void divide(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (low < high) {
// 左边
divide(a, low, mid);
// 右边
divide(a, mid + 1, high);
// 左右归并
merge(a, low, mid, high);
}
}
// 合并
public static void merge(int[] a, int low, int mid, int high) {
int[] temp = new int[high - low + 1];
int i = low;
int j = mid + 1;
int k = 0;
// 按照从小到大排列
while (i <= mid && j <= high) {
if (a[i] <= a[j]) {
temp[k] = a[i];
k++;
i++;
} else {
temp[k] = a[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
// 把左边剩余的数移入数组
while (i <= mid) {
temp[k] = a[i];
k++;
i++;
}
// 把右边边剩余的数移入数组
while (j <= high) {
temp[k] = a[j];
k++;
j++;
}
// 把新数组中的数覆盖原数组
for (k = 0; k < temp.length; k++) {
a[k + low] = temp[k];
}
}


# Trees
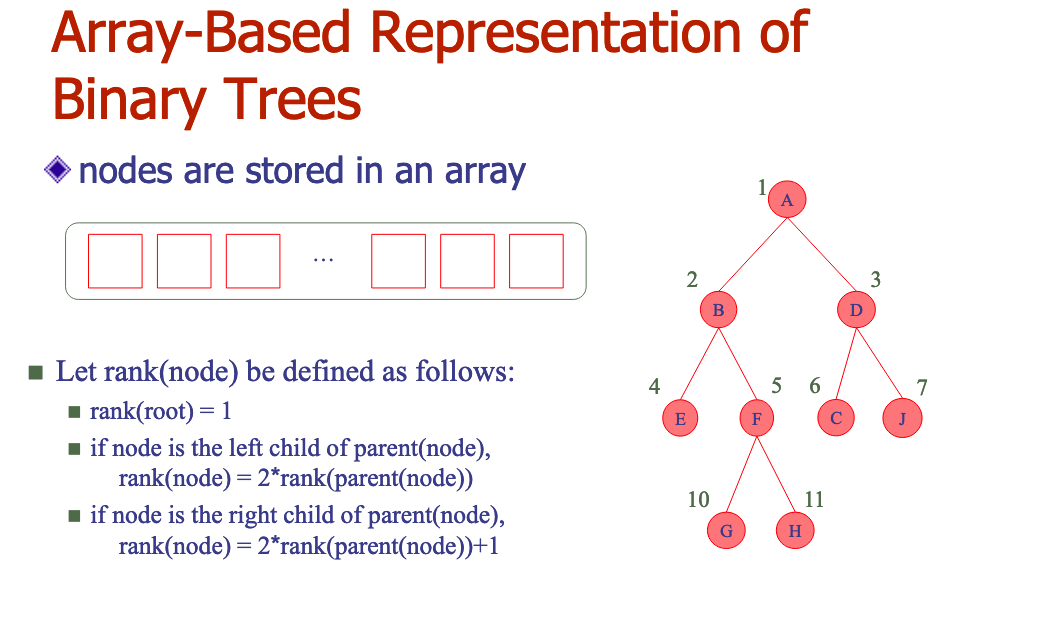
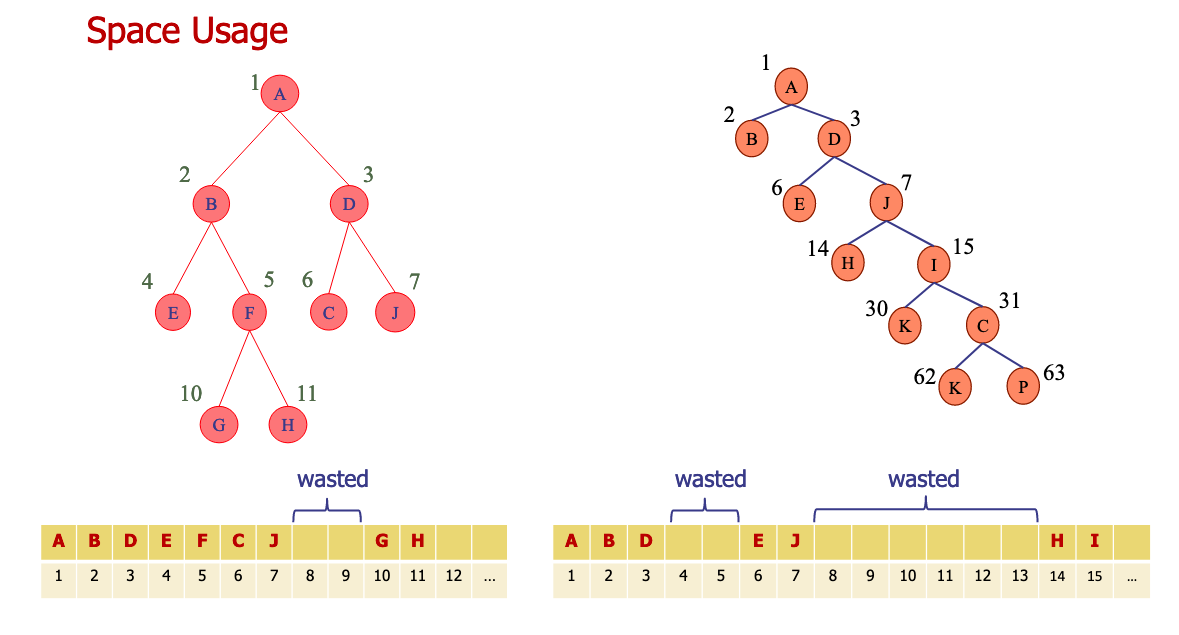
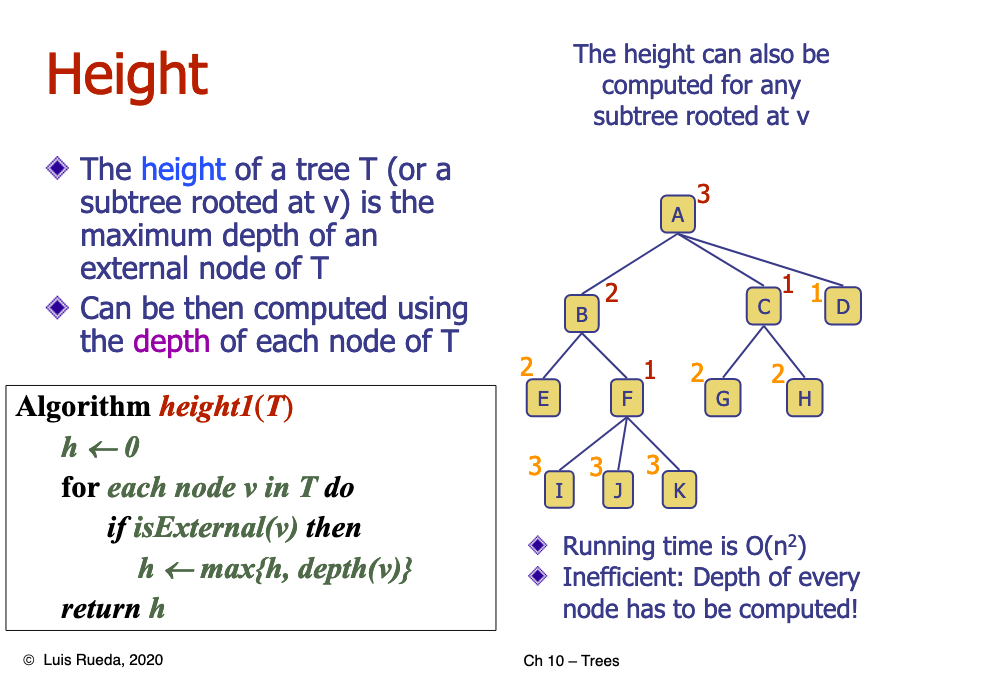
# 1.Give an example of a tree and identify the root, internal and external nodes. Find the depth and height for all nodes in the tree. Do the same for a subtree.

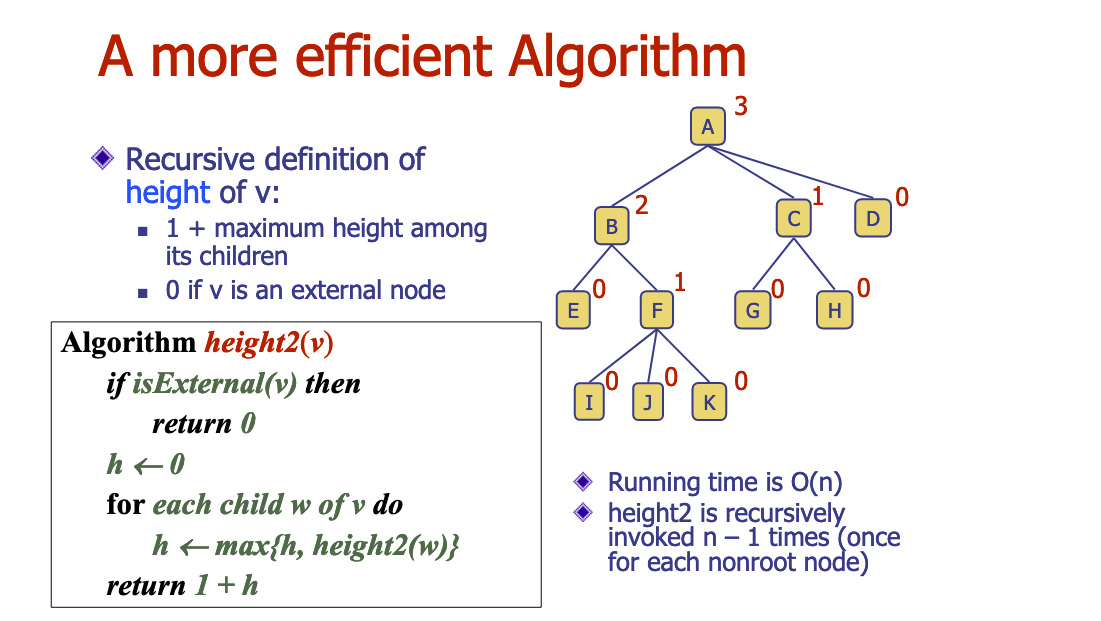
# 2.Why does height2 run in O(n)? Justify.
# 3.Write an algorithm that shows the nodes of a tree from “right to left”, in preorderand postorder traversal. Show that your algorithms run in O(n).
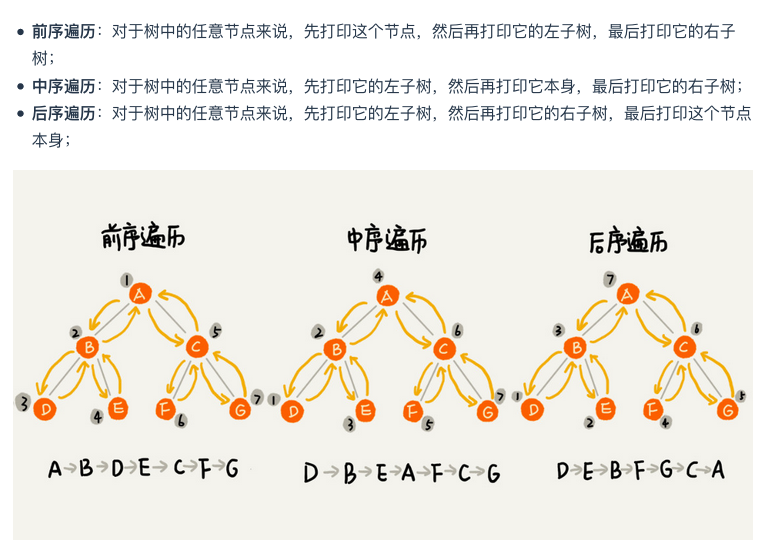
void preOrder(Node* root) {
if (root == null) return;
System.out.print(root->value);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
void inOrder(Node* root) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root->left);
System.out.print(root->value);
inOrder(root->right);
}
void postOrder(Node* root) {
if (root == null) return;
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
System.out.print(root->value);
}

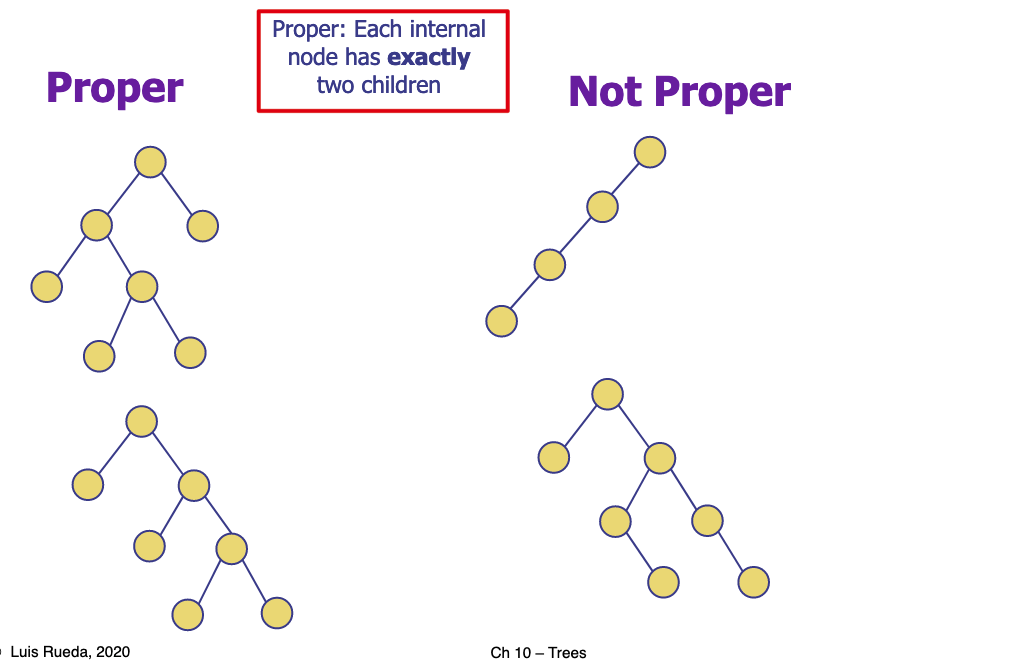
# 4.Give examples of proper and non-proper binary trees.
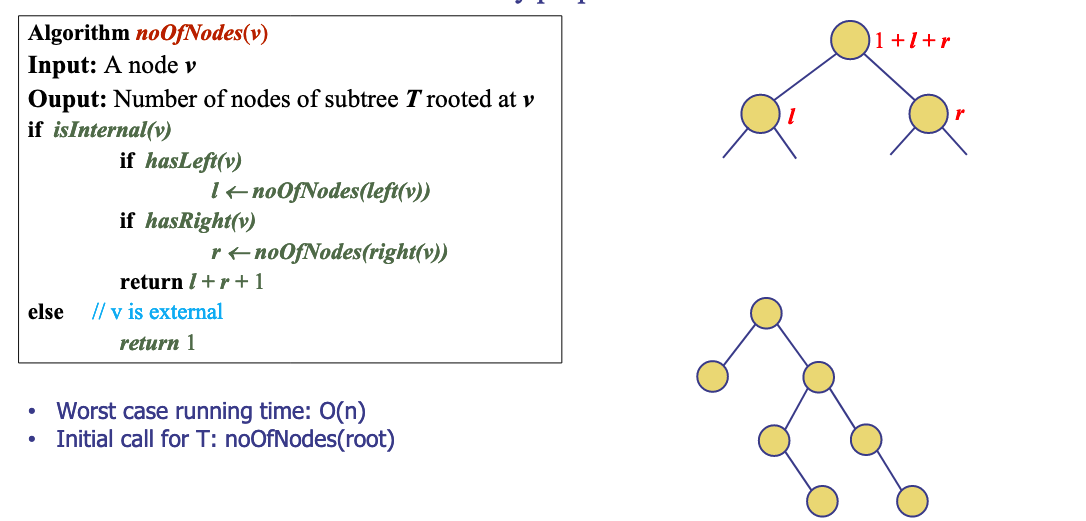
# 5.Why does noOfNodesrun in O(n)? Justify.
# 6.What is the worst-case running time of isProper? Justify.

# 7.Show the properties of binary trees (give a justification for each of them). Give examples.

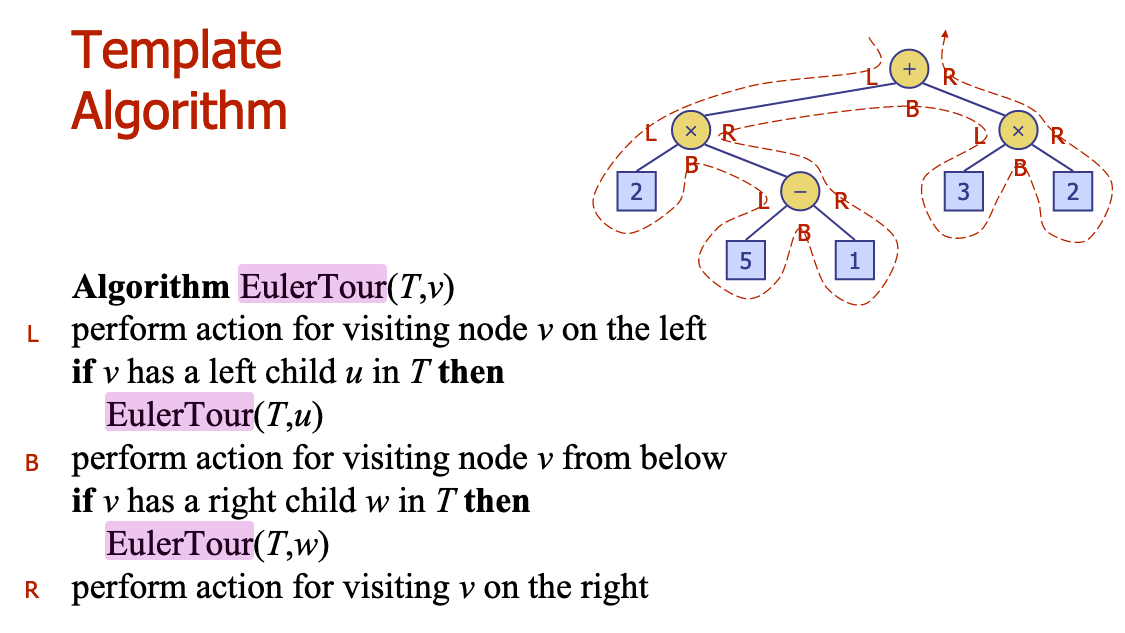
# 9.What is the worst-case running time of EulerTour? Justify. Why isn’t it different from inOrder/preOrderor postOrder?
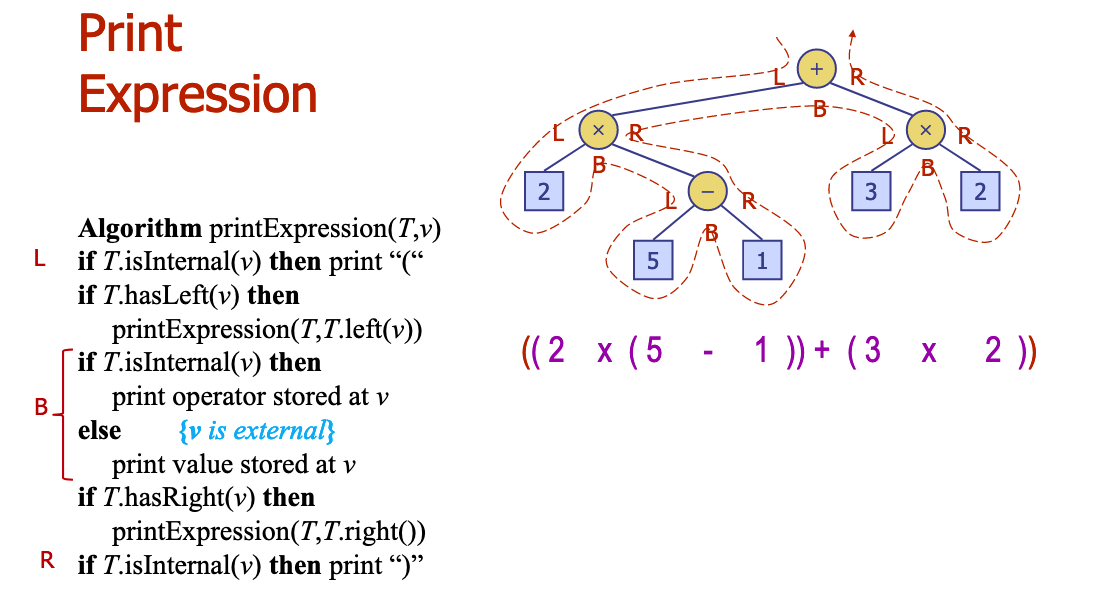
# 10.Modify algorithm printExpressionso that it prints the expression in reverse order.
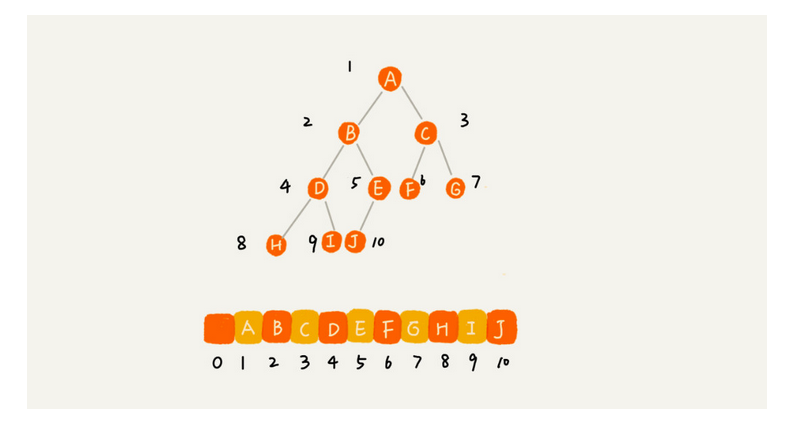
# 11.Write an algorithm that implements a tree on an array. Using that tree, implement the arithmetic expression problem.